Procol • October 10, 2025
The role of procurement strategy in business growth

As we move towards 2025, procurement is advancing to reduce costs, increase compliance, and handle risk and concerns. This blog explains the procurement strategy framework that is important, different kinds of procurement strategies, and the steps to develop a procurement strategy and procurement strategies in different forms. More insight will be provided on global procurement strategies to help develop a future and competitive procurement strategy.
What is the procurement strategy?
Procurement strategy serves as a guide for various methods of purchasing, also known as the purchasing process or purchasing methodology. It helps in economic and time-effective use of one’s resources, minimizing the exploitation and destruction of one’s resources. The procurement strategy governs the supplier management, contract usage, expenditure management, and risk management while making sure that every procurement decision made within the business is consistent with its mission and all the workforce it interfaces with. The right procurement strategy supports savings and reduces the cost of doing business.
Why do you need a procurement strategy?
A procurement strategy is essential for businesses to align sourcing practices with overall organizational goals. Without a defined plan, companies may face inefficiencies, cost overruns, and unreliable supplier partnerships.
- Ensures a structured approach to sourcing goods and services.
- Reduces risks of higher costs, supply chain disruptions, and compliance issues.
- Builds strong, reliable, and accountable supplier relationships.
- Improves Spend Management and identifies opportunities for cost savings.
- Enhances risk management practices across the supply chain.
- Focuses on long-term value creation instead of short-term cost reductions.
- Drives sustainability, innovation, and growth initiatives.
- Strengthens business efficiency and competitiveness.
A well-designed procurement strategy goes beyond reducing expenses—it becomes a driver of value, resilience, and growth. By combining cost efficiency with innovation and sustainability, procurement plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s long-term success.
Top 15 procurement strategies
In today’s ever-changing business reality, having a thorough procurement strategy is crucial for productivity, efficiency, cost reduction, and risk mitigation. The procurement strategy cultivates supplier relationships, aligns with long-term planning for the organization, and enables better purchasing decisions now and into the future as these strategies become more intense involving digital sources, sustainable sourcing, and global procurement.

Cost reduction strategy
Reducing cost while delivering quality products is achievable as long as you are focused on negotiations, bulk buying, and competitive bidding.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong supplier relationships facilitate trust, reliability, and potential for collaborative growth.
Risk Management Strategy
Knowing all the risks that impact procurement is critical, and identifying pathways of least resistance to help mitigate and overcome procurement risk. Whether it’s commodity volatility, shortages, or delays, all of these risks loom.
Global procurement strategy
A global procurement strategy unlocks access to new markets, products, and costs, as well as understanding and remaining compliant.
Sustainable procurement strategy
Sustainable sourcing is environmentally friendly, supports ethical sourcing initiatives, creates a positive brand image, satisfies compliance obligations, and provides organizations with all the good news they need to fulfill their sustainability initiatives.
Innovation-driven procurement
Co-creating products and solutions with suppliers results in new supplier jargon being coined and the development of new technologies and enhancements to products.
E-procurement strategy
Automating procurement through e-procurement digital platforms allows sourcing, bidding, approvals, payments, and other procurement services, while reducing errors and delays.
Category management strategy.
Organizing and managing spend in categories (IT, raw materials, etc.) allows for better supplier optimization and for cost savings from gaining volume discounts.
Supplier Diversification Strategy.
Avoiding single-supplier dependency limits risk and ensures competitive pricing.
Quality-focused procurement
Ensuring sufficient quality standards in procurement prevents defects, increases reliability, and quality assurance protects brand trust.
Agile procurement strategy.
Procurement with a flexibility mindset means you do not have to look at the organization’s original price, but instead look at the current market price, instead of necessarily going through a formal bid process, and consider price changes because data standards are set.
Local sourcing strategy
Working with local suppliers decreases shipping times, reduces logistics costs, and supports local economies.
Collaborative procurement strategy.
Collaborative purchasing makes more resources and expertise available across teams, assisting in better procurement outcomes and more savings.
Ethical procurement strategy.
Procurement accountability through responsible sourcing protects a corporate business’s status, reputation, and compliance with labour and social standards.
Data-driven procurement strategy
Using data insights and analytics, and spending data reads allows procurement decisions to be more intelligent, accurate, and provides predictive capabilities based on data, and can help in the scope of suppliers through ongoing benchmarking.
By adopting these 15 procurement strategies, organizations can transform procurement from a cost-saving function into an enabler of a growth company. Whether through sustainability, technology, or risk management, strong procurement practices strengthen long-term efficiency, resilience and competitiveness. Businesses that prioritize strategic procurement will be much more prepared and adaptable in an evolving global economy.
Types of procurement strategies
Organizations can develop a procurement strategy plan using several different approaches, depending on their objectives, business sector, and supply chain constraints. A sound procurement strategy framework ensures that purchasing decisions align with objectives and strike a balance between cost and efficacy.
The following are the five most effective types of procurement strategies used by companies around the globe in 2025.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost reduction strategy | Aims at lowering procurement costs by negotiating with suppliers, buying in bulk, and tendering for competitive quotes while ensuring quality. |
| Supplier relationship strategy | Develops strong, long-term partnerships with suppliers to reduce risk, increase reliability, increase collaboration, and enhance innovation. |
| Risk management strategy | Recognizes and mitigates supply chain risks, including disruptions, price fluctuations, and compliance issues. |
| Global procurement strategy | Captures benefits provided by international suppliers for better cost, better quality, and new market opportunities. |
| Sustainable procurement strategy | Focuses on utilizing sustainable and socially responsible suppliers to ensure compliance with sustainability standards. |
These five procurement strategies will provide a solid foundation for a resilient and competitive supply chain.
Procurement strategy framework
Procurement has transformed into far more than simply buying goods and services for the least amount of money; it has become a strategic function designed to enable efficiencies, drive innovation and create long-term value. To meet the demands of today’s competitive and dynamic business environment, organizations need an overarching framework for their procurement strategies to bring structure, direction, and alignment with their business goals.
Let’s discuss what a procurement strategy framework looks like and how it can be utilized to enable an organization’s procurement function to attain its desired goals of streamlining sourcing, supplier management, risk mitigation, regulatory compliance, and ultimately, business growth and sustainability.
1. Business alignment
When building a successful procurement strategy, the first step is to ensure business alignment between the strategy and the organization as a whole. Procurement strategies need relevant objectives and KPIs to be directly applicable to business priorities, i.e., cost, sustainability, risk reduction, innovation, etc..
2. Spend analysis
Identifying where money is being spent and identifying opportunities for cost-saving is fundamentally important. This is where a spend analysis can assist organizations in revealing lags in spending, revealing supplier consolidation opportunities, and being more accurate with forecasting procurement needs over the coming years.
3. Supplier market analysis
Understanding the landscape for suppliers is essential for gaining a competitive advantage. Having assessments on benchmark behaviour, risk types, and stakeholder behaviours and sourcing intentions when investigating competitive filtering and adapting plans based on market trends can be some of the methods available to drive better sourcing decisions.
4. Category management
By developing categories to divide procurement, organizations can apply specific practices to each category. For instance, some categories are better served by competitive bidding while others can benefit more from long-term strategic partnering.
5. Risk & compliance
Concerns about compliance and disrupted supply chains will continue to grow. An effective framework will include checks, its ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) aspirations, and contingency plans to mitigate risks and decrease exposure.
6. Sourcing strategy
The organization must choose how centrally or decentralized the sourcing process will be internally. It will have to work with its employees to have selection criteria for suppliers, negotiations, contract management process, and internal sourcing process, as it sees fit to provide the organization with positive value that is effective and efficient.
7. Supplier relationship management (SRM)
Key strategic suppliers can drive long-term partnering, deeper collaborative relationships, enhanced quality and efficiency, and create more innovation. A well-designed SRM strategy adds value for both parties by sustaining trust, establishing continuous improvement ideals, and driving shared value.
8. Technology & digital tools
Digital procurements are rapidly changing the way organizations conduct operations. Digital tools such as e-procurement, AI-derived spend analytics, and eliminating paper-driven processes provide organizations with better visibility, make faster and better decisions, and save costs.
9. Sustainability & value creation
Today’s expectations of procurement go beyond value from decreased costs. Green procurement, ethical sourcing, and total cost of ownership accounting will enable organizations to create value that is long-term, sustainable, and meets the surrounding expectations of customers and stakeholders.
10. Ongoing monitoring & improvement
Procurement strategies must adapt to evolving market conditions and changing business objectives. Enhanced performance reviews, supplier evaluations, and KPI monitoring will allow organizations to pivot and continuously improve.
A procurement strategy framework is not a one-size-fits-all framework; it must be created for each organization separately based on its industry, size, and goals. Organizations that emphasize Alignment, Analysis, Risk Management, Technology, and Continuous Improvement can make procurement a full strategic contributor and driver of business success.
Global procurement strategy
Businesses today are no longer limited to local suppliers in a global economy. Organizations adopting global procurement strategies to buy products or services anywhere in the world aim to lower costs and provide access to innovation and more robust supply chain resilience.
A global procurement strategy is not simply buying from abroad; a global procurement strategy is a structured approach to aligning procurement with the organization’s broader objectives. A global procurement strategy prepares organizations to identify reliable global suppliers. It considers the total cost of ownership (TCO) and compliance. And assesses risks from currency fluctuations, geopolitical events, and logistics.
A successful global procurement strategy must address the various components: market intelligence; supplier relationship management; cost containment; sustainability; and digital tools and disruptive technologies like e-procurement, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain. Digital tools and disruptive technologies can build visibility as well as enhance strategic decision-making on an international basis.
The benefits to organizations that adopt global procurement strategies are considerable and provide more extensive supplier networks, preferable pricing, improved economies of scale, and increased opportunities for innovation. The other side of expanded opportunities is the need to address the challenges of cultural barriers, trade regulations, and longer lead times when establishing new supplier relationships.
By learning to balance opportunities against risks, organizations can effectively and strategically exploit global procurement to enhance efficiency, resilience, and long-term value creation. In the future, all sustainable and digital transformations will continue to define successful global procurement strategies.
Sourcing strategies in procurement
Sourcing is a fundamental process of procurement, which can significantly impact the reduction in expenditure, supplier relationships, and resilience in the supply chain. The ability to develop an optimized sourcing strategy means organizations obtain grassroots costs to manage; it also means creating long-term value through risk management, sustainability, and innovation. Sourcing should consider multiple factors. The strategies are as follows:
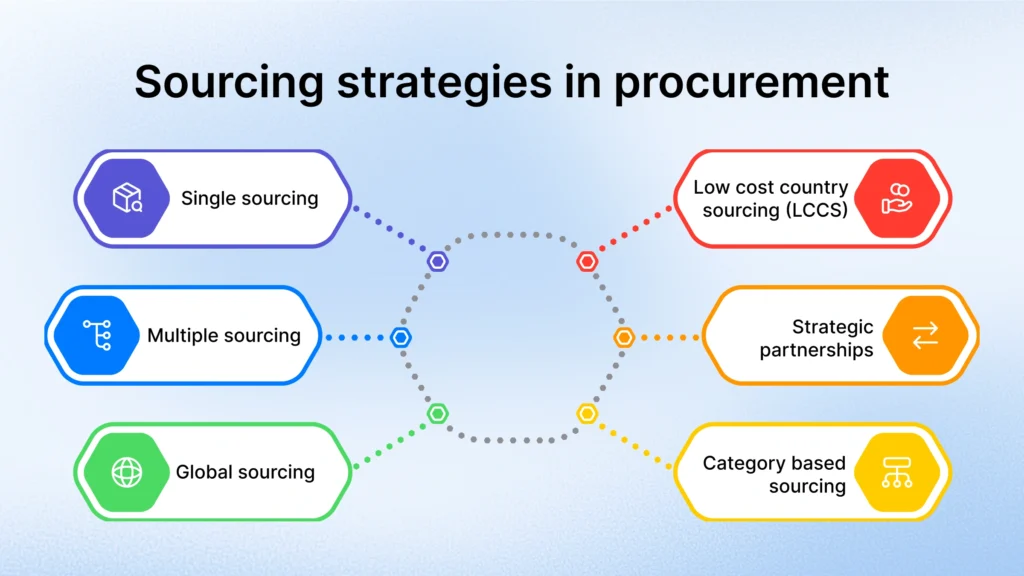
1. Single sourcing
Using one supplier for one category to create consistent representations among the supply base, foster relationships, and have consistent pricing. Risk is using only one source supplier.
2. Multiple sourcing
Engaging with multiple suppliers to lessen risk, competition, and ensure supply.
3. Global sourcing
Seeking resources in international markets to acquire low-cost, specialized suppliers, or create sustainable innovation and benefits, whilst also managing logistics and fulfilling compliance risks.
4. Low-cost country sourcing (LCCS)
Outsourcing the production and or purchasing for a country to generate cost savings through cheaper labor and materials.
5. Strategic partnerships
Involving key suppliers to collaboratively explore opportunities for innovation and efficiencies that deliver more than just procurement savings.
6. Category-based sourcing
Dividing spend into categories that apply unique sourcing methods suited to achieve the most successful overall results.
The ability to select the effective sourcing methods for the procurement organization depends on organizational objectives, appetite for risk, and the state of the market. Procurement organizations should have a portfolio of sourcing methods in order to deliver efficient, cost-effective, and sustainably responsible supply chain performance.
Conclusion
The future of procurement strategy will go beyond cost savings and evolve to drive business resilience, sustainability, and innovation. As global supply chains become increasingly complex, organizations will rely on digital, AI, blockchain, and predictive analytics to provide visibility, direct decision-making, and encourage proactive risk management. Sustainability and ethical sourcing will become key areas of attention, with procurement teams expected to align strategic capacity with ESG objectives and stakeholder values. Continued innovation will stem from partnerships with suppliers rather than transactional relationships. Future procurement strategies will therefore be agile, collaborative, data-driven, and sustainable; ultimately enabling businesses to thrive in a more complex, unpredictable, and connected world.
Frequently asked questions
What is a procurement strategy and why is it important?
A procurement strategy is a long-term plan that guides how an organization sources, negotiates, and manages suppliers. It goes beyond buying at the lowest price—it ensures value creation, risk reduction, supplier reliability, and alignment with business goals. Without a clear strategy, companies risk overspending, supply chain disruptions, and missed opportunities for innovation.
What role does sustainable procurement play in modern strategies?
Sustainable procurement (or green procurement) has become central to modern business strategies. By selecting eco-friendly suppliers, reducing waste, and considering lifecycle costs, companies not only minimize their environmental footprint but also strengthen brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements. Many organizations now treat sustainability as a competitive advantage rather than a compliance measure.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid in procurement strategy?
Businesses often fail when they:
-
Focus only on cost savings and ignore long-term value.
-
Rely too heavily on one supplier, creating supply chain risks.
-
Neglect supplier relationship management.
-
Delay adopting digital procurement solutions.
-
Ignore sustainability, missing out on regulatory and market advantages.
Explore more from Procol
Discover expert tips, how-to guides, industry insights, and the latest procurement trends.

What is supply chain risk management (SCRM)? | Definition & steps
In an increasingly interconnected world, organizations rely on smooth supply chain...

Strategic sourcing management software & sourcing solutions: a guide
Learn how strategic sourcing software helps optimize processes, key features and...

Sourcing strategies explained: Types, process, benefits, and examples
Sourcing strategies are important for creating effective, efficient, and resilient supply...







