Rutuparna Rout • January 29, 2026
Supplier relationship management strategies : The complete guide

Last update: January 12, 2026

In today’s complex business environment, successful operations depend heavily on strong, functional relationships with external partners. Supplier relationship management strategies are core business practices designed to enhance collaboration and communication with companies that provide goods and services. Effective supplier relationship management strategies are not just about securing the lowest price; they are about creating mutual value, reducing risk, and driving innovation throughout the supply chain.
This document will explore the fundamental aspects, steps, benefits, and future direction of effective supplier relationship management strategies.
What are supplier relationship management strategies?
Supplier relationship management strategies are the planned, structured approaches companies use to manage and optimize interactions with suppliers for mutual benefit. These long-term approaches aim to maximize value by treating key suppliers as strategic partners rather than merely transaction partners. An effective srm strategy involves segmenting suppliers, establishing joint performance goals, and investing in tools to build resilient, collaborative partnerships that ensure supply continuity and drive innovation.

Why are SRM strategies essential?
SRM strategies are crucial for modern businesses, as they underpin sustained growth, quality, and resilience. They are essential for the following reasons:
1. Maximize Value Beyond Cost Savings
- Unlock Innovation: Deep partnerships enable businesses to leverage their suppliers’ expertise, resulting in co-developed solutions, product innovation, and process improvements.
- Achieve Efficiency: Through collaborative efforts, organizations can achieve cost reductions that extend beyond simple price cuts, such as leveraging shared economies of scale and implementing joint cost-reduction initiatives.
- Elevate Procurement’s Role: SRM shifts the procurement strategy from a cost center to a strategic value creator and business partner, giving the team a “seat at the table” with executive leadership.
2. Ensure Supply Chain Resilience and Stability
- Mitigate Risk: Strong relationships provide greater visibility into the supply chain, enabling anticipation and mitigation of financial instability, quality issues, and geopolitical risks.
- Increase Agility: Closer communication and alignment enable faster response to market changes, supply shortages, and unforeseen events such as natural disasters and pandemics.
- Secure Loyalty: By acting as a “Customer-of-Choice”, a company is prioritized for scarce capacity or resources during times of industry disruption.
3. Drive Quality and Compliance
- Improve Product Quality: Collaborative relationships lead to shared quality standards, testing procedures, and better consistency in delivered goods and services.
- Protect Brand Reputation: SRM helps identify and monitor suppliers’ ethical practices, ensuring compliance and avoiding association with human rights or environmental controversies that could tarnish your brand.
4. Facilitate Continuous Improvement
- Enable Ongoing Optimization: SRM establishes a continuous cycle where performance is consistently monitored, feedback is provided, and joint improvement plans are developed.
- Establish Clear Governance: Supplier agreements are more than contracts; they are strategic blueprints that outline expectations, risk management protocols, and clear structures for quality assurance and dispute resolution.
What are the top 12 supplier relationship management strategies in 2025?
Supplier management is the process of selecting and managing suppliers or vendors. It directly impacts your business costs, manufacturing, and cash flow. Global supply chains are increasingly complex, making supplier relationship management more challenging and essential.
To solve the pattern of supplier relationship management, you are getting the best from your suppliers while building strong relationships that deliver tangible benefits. The following strategies will help you improve your supplier management and achieve your business goals:
1. Set Strategic Objectives and Establish KPIs
Define your supplier management goals based on business needs, focusing on cost, supply chain efficiency, and resilience. Use KPIs to measure your suppliers’ actual performance.
Common KPIs include the following parameters:
- Defect rate: How well products or services meet quality standards
- Lead time: Time taken to fulfill orders
- Order accuracy: Correctness of orders in terms of items and quantities
- Competitiveness: Supplier costs compared to competitors
- Customer service: Quality of supplier support and responsiveness
2. Adopt a Centralized Supplier Management Database
A centralized digital supplier management tool is essential for businesses with complex supply chains. This can be achieved through the following parameters :
- Supplier Information Management (SIM): Capture, store, and analyze supplier data to reduce administrative work and improve data accuracy
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Manage suppliers and build more productive relationships through structured processes
3. Improve Your Supplier Risk Assessment Process
Your suppliers can pose significant risks to your business through the following parameters :
- Financial risks: Supplier bankruptcy, inability to handle increased volumes, or sudden cost increases
- Legal risks: Contract non-compliance, intellectual property misuse, and lawsuits
- Operational risks: Quality control issues, disruptions, and manufacturing delays
- Reputational risks: Product safety issues or failure to follow ESG principles
4. Strengthen Your Supplier Onboarding Process
Create a smooth onboarding experience to build strong relationships from the start through the following parameters :
- Collect necessary information and documentation for compliance and risk assessments
- Register suppliers on internal systems efficiently
- Best practices include automating processes wherever possible, maintaining a consistent approach across all suppliers, and ensuring supplier data security against breaches.
5. Segment Your Suppliers
Categorize suppliers based on their importance to your business through the following parameters :
- Identify and prioritize the most critical suppliers
- Focus resources on relationships that matter most to your supply chain
- Strengthen key relationships for long-term business success
6. Integrate Automation and Self-Service
Use SIM and SRM software to improve efficiency and reduce costs through the following parameters :
- Manage contracts in a single location
- Automate the onboarding process
- Monitor supplier performance automatically
- Offer self-service options for suppliers to input their own data
- Reduce overheads while keeping records accurate and up to date
7. Streamline Communication Channels
Build strong relationships through clear and open communication through the following parameters :
- Use direct messaging and document-sharing tools
- Provide platforms where suppliers can check invoice status
- Link queries to relevant purchase orders, invoices, or payment documents
- Track conversations in a centralized system
- Resolve issues quickly and easily
8. Assess Supplier Performance Regularly
Monitor supplier performance continuously through the following parameters :
- Use KPIs to track performance against agreed standards
- Identify suppliers failing to meet expectations
- Address poor performance through strong relationships
- Renegotiate contracts or escalate issues if performance doesn’t improve
9. Prioritize Strong Supplier Relationships
Invest in long-term supplier relationships so that it can remove some of the factors mentioned below:
- Poor relationship management leads to communication breakdowns, loss of mutual trust, mismatched priorities, complex negotiations, supply issues, and more.
- Strong relationships lead to improved operational efficiency, enhanced supply chain resilience, and smoother collaboration.
10. Formulate Supplier Management Contingency Plans
Prepare for potential disruptions with effective backup plans:
- Identify contingency suppliers to call upon if needed
- Maintain key contact information
- Understand possible lead times
- Protect your business from supplier failure through proactive planning
11. Discover New Suppliers
Build relationships with new potential suppliers to strengthen your supply chain through the following parameters :
- It matters coz 77% of executives reported supply chain disruptions in the previous year, 44% expect more challenges ahead, and supply chain issues, logistics problems, and parts shortages are common.
- Benefits of finding new suppliers include increasing diversity and flexibility in your supply chain, protecting your business against future disruptions, providing backup options when primary suppliers can’t meet your needs, and gaining better negotiating power to secure competitive pricing.
12. Ask for Feedback
Make feedback a regular part of your supplier relationships through the following things :
- Ask the right questions: Find out how you can support them better, improve collaboration, and fix any relationship or process issues. Gather feedback through regular calls, surveys, or direct conversations.
- Catch problems early: Regular feedback shows your commitment to the relationship and helps identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
What is the step-by-step process of supplier relationship management?
Managing vendor relationships successfully requires a strategic, multi-phased approach, with each step playing a crucial role in building and maintaining strong partnerships. Here, we’ll walk you through each phase in detail to ensure you maximize value and streamline collaboration with your vendors.
Step 1: Supplier Segmentation
Supplier segmentation involves categorizing suppliers by strategic importance and the complexity of managing their relationships. Tools that classify suppliers into four categories: strategic, leverage, bottleneck, and non-critical. For example, strategic suppliers are vital to business operations and require close collaboration, while non-critical suppliers typically involve simple, transactional relationships.
Step 2: Establish KPIs and Goals
Setting clear KPIs, such as metrics for cost efficiency, quality, delivery reliability, or innovation, is essential for aligning supplier performance with your organization’s objectives. You should track these KPIs to ensure your suppliers meet the agreed-upon standards, hold them accountable, and drive ongoing improvement.
Step 3: Develop a Supplier Management Strategy
A well-crafted supplier management strategy provides a roadmap for effectively managing your supplier relationships. It may include supplier segmentation and the establishment of parameters for a collaborative partnership focused on the co-development of innovative products and services.
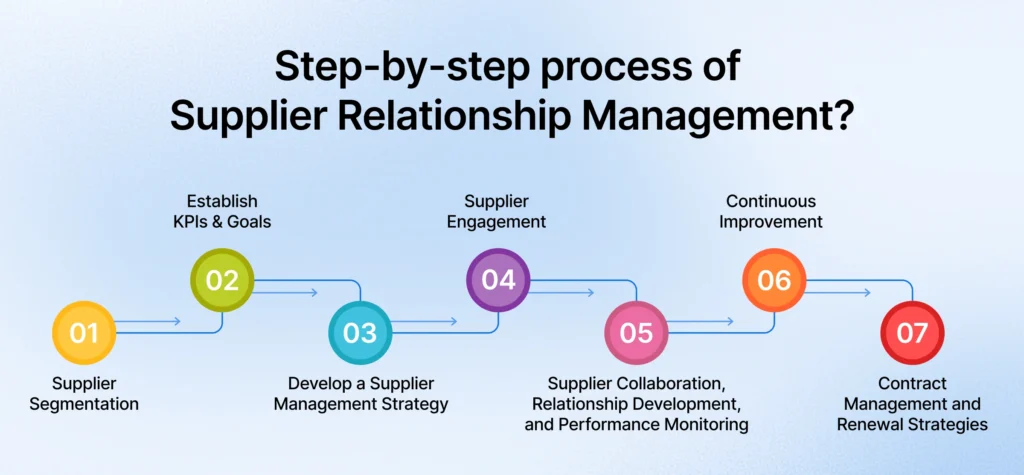
Step 4: Supplier Engagement
Supplier engagement encourages open communication and trust between you and your suppliers with regular meetings and the opportunity to provide feedback. Engaging proactively with your suppliers helps them to align with your goals and goes a long way toward building a long-term partnership that delivers consistent value.
Step 5: Supplier Collaboration, Relationship Development, and Performance Monitoring
Developing strong relationships with suppliers extends beyond transactional interactions; it involves collaborating on mutual goals, addressing challenges together, and sharing insights to enhance SRM processes. Regular performance monitoring is equally essential to tracking KPIs, as it helps identify potential issues and address them proactively.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement
Regular performance assessments and benchmarking against industry standards help identify gaps and areas for enhancement. It’s essential to gather feedback from internal teams and suppliers to gain valuable insights, enabling you to take corrective actions or implement process enhancements when needed. By focusing on continuous improvement, you can ensure that your supplier relationships are aligned with your organization’s evolving needs.
Step 7: Contract Management and Renewal Strategies
Managing contracts includes regular reviews of terms and conditions, performance-based renegotiations, and adjustments to incentivize innovation or address compliance issues. Proactively managing contract renewals enables organizations to solidify partnerships with high-performing suppliers while addressing concerns with underperforming ones.
What are the key benefits of supplier relationship management strategies?
Implementing a structured supplier relationship management process offers numerous advantages. These efforts enable organizations to move beyond simple cost savings and achieve sourcing strategies accordingly. Key benefits include:
Cost Reduction
By collaborating on process improvements and sharing accurate forecasts, organizations can achieve better pricing and more favorable payment terms beyond initial negotiation efforts.
Improved Quality and Reliability
Close partnerships ensure suppliers clearly understand quality expectations, leading to fewer defects and more reliable delivery schedules.
Enhanced Innovation
Strategic suppliers often possess unique expertise. By leveraging strong supplier relationship management strategies, companies can use this knowledge to co-develop new products or enhance internal processes.
Better Risk Management
Proactive monitoring and open communication, facilitated by effective supplier relationship management strategies, enable the detection and mitigation of potential supply chain disruptions, such as financial instability or compliance issues, before they occur.
Preferred Customer Status
When suppliers feel valued, they often prioritize the organization, especially during times of high demand or scarcity, a vital outcome of strong supplier relationship management strategies.
What are the challenges in the supplier relationship management process?
Despite the benefits, implementing strong supplier relationship management strategies can face several challenges:
Lack of Internal Alignment
Different departments (like procurement, operations, and finance) may have conflicting views on a supplier’s importance or performance, primarily because each team prioritizes different metrics that align with its specific functional goals and responsibilities.
Data Silos and Visibility Issues
Supplier information, performance data, and contracts may be scattered across different systems, making it difficult to gain a clear, comprehensive view of the relationship. This often leads to inaccurate supplier segmentation, inefficient decision-making, and increased operational risk due to fragmented data.
Resistance to Collaboration
Some suppliers may prefer purely transactional interactions, making it challenging to implement deeper, more collaborative supplier relationship management strategies, particularly when they lack the necessary resources, motivation, or strategic alignment to invest in joint planning and long-term development.
Complexity of Global Supply Chains
Managing diverse regulatory, cultural, and logistical requirements across international suppliers adds significant complexity to any supplier relationship management strategy, especially given the increased risk of non-compliance, communication breakdowns, and higher transportation and inventory costs associated with global operations.
Difference between the srm strategy vs vendor relationship management strategy
The terms are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference in scope and focus between an srm strategy and a vendor relationship management strategy.
| Feature | Srm strategy | Vrm strategy |
| Purchase | Establishing mutually beneficial business relations with suppliers to maximize long-term value. | Establishing costs and defining service level agreements with vendors to ensure basic compliance and execution. |
| Contract Type | Strategic. Involves identifying long-term gains for both parties. | Generally Transactional. Parties may negotiate pricing and terms, but the scope of the relationship is limited. |
| Risk | Supplier risks pose a long-term, strategic impact on enterprises, as it is often difficult to find a replacement. | Vendor risks impact an organization in the short term, as they are straightforward and less disruptive. |
| Relationship | Primarily defined by the contract, the interaction scope is limited to contractual terms. | Focused on maximizing value beyond the contract through engagement and shared strategic goals. |
How to choose the right supplier relationship management plan?
Choosing the right supplier relationship management plan requires careful self-assessment and alignment with organizational goals.
Define Business Objectives
Start by identifying what you need most: cost savings, risk mitigation, or innovation. Your supplier relationship management plan must directly support these primary objectives.
Segment the Supply Base
Use a framework to determine which suppliers are strategic. Focus your most intensive efforts and resources on these high-impact relationships.
Assess Current Capabilities
Evaluate your existing technology and team skills. Do you have the tools for real-time performance tracking and a central data repository?
Prioritize Technology Needs
Select a system that aligns with your complexity. If your supply base is complex, you need an advanced supplier relationship management plan supported by comprehensive software.
Start Small and Scale
Implement the supplier relationship management strategy with a select group of strategic suppliers first, measure the results, and then expand the program to other segments.
What are the key tools for supplier relationship management strategies?
Modern procurement relies heavily on technology to successfully implement a wide-ranging srm strategy. The tools used for this effective strategy are often integrated software suites that centralize data and automate workflows.
SRM Software Platforms
Dedicated software solutions (like those from Ivalua, GEP, or SAP) that provide end-to-end functionality for segmentation, performance management, and collaboration.
Supplier Portals
As mentioned above, these are the primary interfaces for managing communication and data exchange with suppliers.
Risk Management Tools
Specialized modules that monitor external factors (like financial health, geopolitical issues, and ESG compliance) to provide real-time risk alerts.
E-Sourcing and Contract Management Systems
Tools that manage the entire contract lifecycle, from creation and negotiation to renewal, ensuring that the contractual basis of the srm strategy is always clear.
Data Analytics and Scorecarding Tools
These generate customized reports and dashboards using real-time data to evaluate performance metrics (OTIF, quality, cost) for all supplier relationship management strategies.
What is the future of the supplier relationship management framework?
The future of the supplier relationship management framework will be shaped by increased automation and advanced data analytics. Key trends include:
AI and Machine Learning
AI will automate supplier segmentation, predict & manage supply chain risk management before they materialize, and suggest optimal communication strategies for different suppliers.
Deep Integration
SRM platforms will be deeply integrated with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and other core business systems, enabling seamless data flow from finance to operations.
Focus on ESG and Sustainability
Future supplier relationship management strategies will place a strong emphasis on tracking Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance, requiring suppliers to meet higher standards of ethical and sustainability practices.
Prescriptive Analytics
SRM systems will move beyond simply reporting performance to offering prescriptive advice on specific actions needed to improve a relationship or mitigate a developing risk. This ensures a proactive supplier relationship management framework is in place.
What are the components of Supplier Relationship Management?
The goal of components is to transform purely transactional exchanges into strategic, mutually beneficial partnerships. There are five essential components of an inside supplier relationship management strategy that mainly focus on strategic value creation and supply chain resilience.
1. Categorizing Suppliers
This component involves supplier segmentation, a strategic process that enables effective resource allocation. By categorizing suppliers based on their potential to influence efficiency and profitability, organizations can focus their efforts on high-value partnerships to maximize value creation rather than solely on basic performance metrics.
2. Measuring & Improving Supplier Performance
Effective evaluation moves beyond mere compliance to use holistic performance metrics. This involves considering factors such as innovation contribution, sustainability practices, and risk mitigation. Real-time monitoring, customized scorecards, and a focus on teamwork ensure continuous improvement and resilience in the MRO supply chain.
3. Becoming a Better Customer
Securing the best supplier resources, innovations, and services requires achieving most-favored customer status. This is accomplished by deeply understanding the supplier’s perspective, aligning on long-term growth goals, and implementing strategies such as transparent data sharing, streamlined communication, and prompt payments.
4. Collaborating with Suppliers
Collaboration is the cornerstone of a high-performing supply chain, signifying a deep-rooted partnership with a shared vision. True collaboration transcends mere cooperation to achieve superior collective outcomes. It unlocks value through enhanced visibility, swift problem remediation, and overall cost containment.
5. Improving Supplier Quality
Substantial quality enhancement stems from a cooperative strategy that includes consistent investment in supplier meetings and the effective capture and exchange of product failure data across various client environments. Utilizing purpose-built tools for warranty management and maintenance enables a data-driven approach to continuous quality improvement.
What are the best practices for an effective srm strategy?
By focusing on management and strategic alignment, organizations can secure access to scarce resources, improve quality, and enhance overall business value.
Here are the key best practices for effective supplier relationship management:
Strategy vs. Scorecard
SRM is a strategic partnership to enhance supplier value, not just a performance scorecard. Utilize supplier segmentation to focus efforts and tailor metrics to distinguish between strategic and operational suppliers. Scorecards must include non-operational metrics, such as resilience and sustainability, for your most critical partners.
Collaboration
Collaboration yields improved cost, quality, and priority access to scarce resources. Implement a structured four-step process encompassing strategy design, stakeholder alignment, communication, and governance. Differentiate between operational collaboration and strategic collaboration.

Supplier Innovation
Actively partner with key suppliers to leverage their expertise and resources for innovation. The ability to co-create solutions is crucial for navigating disruptions and driving future competitiveness in the supply chain.
Supplier Quality
Shift quality focus from fixing past failures to anticipating future problems. Use leading indicators in assessments, such as technical expertise and change control management effectiveness. Reward high performance and enforce clear consequences for underperformance.
Strategic Partnership
Strive to be a customer of choice by demonstrating trustworthiness and respecting margins. Maintain an open feedback loop to foster transparency and ensure you address internal issues that may impact supplier performance.
Why choose Procol’s supplier relationship management in procurement?
Choosing a specialized solution like Procol for supplier relationship management in procurement can offer distinct advantages, particularly for organizations seeking a digital-first, streamlined experience.
Its features often emphasize streamlining the supplier qualification and approval process, a common pain point in supplier relationship management, through accelerated onboarding. Another feature is real-time risk mitigation, which continuously monitors and alerts the procurement team to potential risks, enabling proactive action.
Rather than these features, it also centralizes all data from contracts, performance scores, and risk profiles in one location, which is crucial for making informed decisions regarding supplier relationship management strategies. It also provides a user-friendly interface that enables both the organization’s team and suppliers to manage tasks and communicate easily from any device, thereby ensuring high adoption of the supplier relationship management portal. Procol supports comprehensive supplier relationship management strategies by automating key workflows.
Conclusion
Effective supplier relationship management strategies are fundamental to a resilient, high-performing supply chain. By clearly defining your srm strategy, segmenting suppliers, and investing in the right technology, organizations can transform transactional exchanges into value-generating partnerships. A well-managed supplier relationship plan and process delivers numerous benefits, including significant cost reductions and enhanced innovation. These strategic efforts are beneficial for effective procurement and supply chain management.

Frequently asked questions
What are the top 5 crucial components of a supplier relationship management strategy?
The top 5 crucial components of a supplier relationship management strategy are supplier segmentations and categorization, performance measurement and KPIs, collaborative communication and engagement, risk management and mitigation plans, continuous improvement and innovation initiatives.
What are the supply relationship management examples?
Examples of supply relationship management include joint innovation programs with key suppliers, performance scorecards and regular business reviews, collaborative cost-reduction initiatives, early supplier involvement in product development, and strategic partnerships for long-term supply security.
What is supplier relationship management technology?
Supplier relationship management technology is a software that helps organizations manage supplier interactions, track performance, automate workflows, assess risks, and analyze supplier data to enhance collaboration and informed decision-making.
What capabilities are necessary for supplier relationship management technology?
The capabilities necessary for supplier relationship management technology include supplier performance monitoring, contract management, risk assessment and mitigation, collaboration tools, spend analytics, compliance tracking, and integration with procurement and ERP systems.
What are the challenges in supply chain management strategies?
Supply chain management strategies face several key challenges, including unpredictable demand and economic shifts, rising costs and labor shortages, and disruptions from port congestion, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters.
How do ERPs support srm strategy?
ERPs support srm strategy by centralizing transactional data such as purchase orders, invoices, and payment histories, creating a single source of truth for performance and tracking. They enable automated workflows and integrate with dedicated SRM modules for risk monitoring and supplier communication.
How can srm elevate the role of procurement?
The srm makes procurement more strategic. Instead of just focusing on buying things at lower prices, supplier relationship management strategies turn the team into a source of value and ideas. This new role allows procurement to drive innovation and become a key business partner, giving them a bigger voice with executives.
Schedule a Demo
We’d love to hear from you. Please give us a call on +1 315-645-2799.
Explore more from Procol
Discover expert tips, how-to guides, industry insights, and the latest procurement trends.

Procurement orchestration: All you need to know in 2026
Explore the value of procurement orchestration, how it works, its benefits,...

Top 22 spend management KPIs to optimize procurement in 2026
Today’s business world has moved from just ‘buying’ to ‘managing spend’...

What is supplier diversity and why is it important?
In the modern corporate competitive world, where both market resilience and...









